Carotid Artery Disease – Stroke
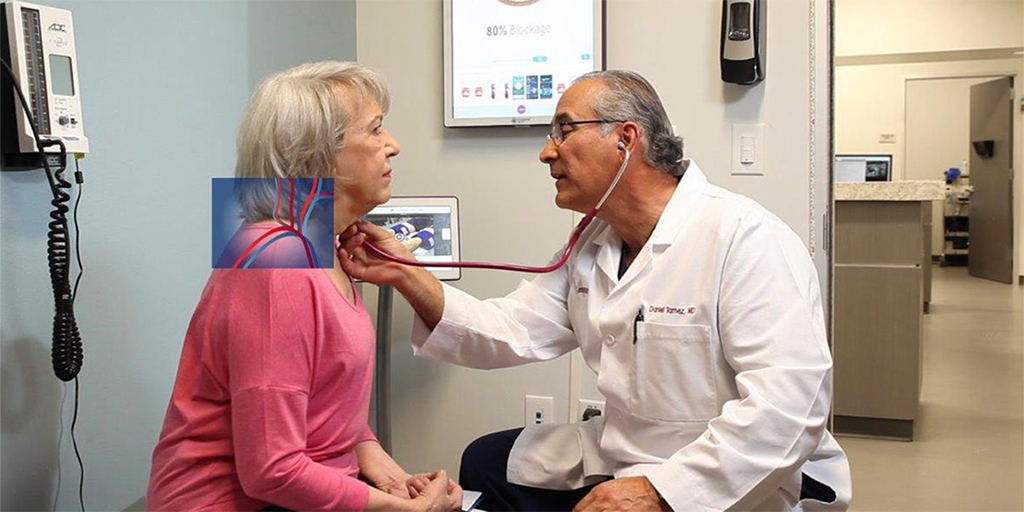
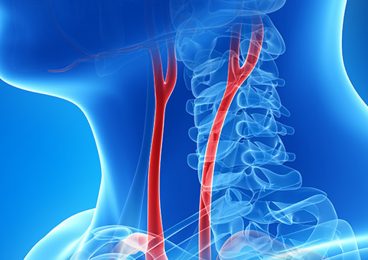
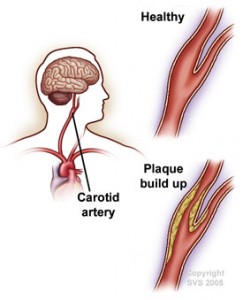
The two main arteries in the neck carry blood from your heart to your brain. Carotid artery disease occurs when there is a build up of plaque in these arteries. In addition, Carotid artery disease is a cause of stroke.
Plaque is a sticky substance of cholesterol, calcium and fibrous tissue which can have a crumbling characteristic like broccoli or cauliflower. When pieces of plaque break off into the bloodstream they can block blood flow to the brain and cause a section of the brain to stop functioning. Quickly restoring blood flow can prevent brain cell death or damage. If no brain cells are lost, the episode is a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA). A stroke, commonly referred to as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), may result in long-term disability or even death. Some patients, thankfully, have complete recovery from a stroke. However, patients with untreated conditions will likely suffer another TIA or stroke. In general, the more severe the stenosis in the carotid artery, the higher the risk for stroke.
Who is at Risk?
People with a history of smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes. People with cardiac disease are also at risk for carotid disease. Another group of risk factors, known as metabolic syndrome, includes having abdominal obesity, high triglyceride level (a type of fat in the blood), low level of HDL (“good”) cholesterol, high blood pressure and high blood sugar.
Symptoms
You may not experience any symptoms of carotid artery disease. Your doctor will use a stethoscope to listen for a bruit which is the sound of blood rushing. Patients may experience weakness or complete loss of muscles function in either the left side or right side of the body or face. Slurred speech, one sided facial drooping, or amaurosis fugax, loss of vision in one eye for a few minutes, are other common symptoms. Blockage of blood to the retina causes amaurosis fugax.
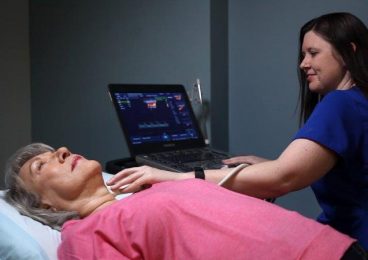
Tests
The most common test for evaluating carotid artery occlusive disease is duplex ultrasound. However, a less specific but also useful test is the magnetic resonance angiography and CT angiography. Catheterization of the arteries with injection of x-ray contrast helps to fully evaluate all of the blood vessels that supply the brain with arterial blood flow, including the aortic arch, the carotid arteries, the vertebral arteries and the arteries inside of the brain. In other words referred to as a four vessel cerebral angiogram.
Testing can be done in the PVA Vascular Lab.
Treatments
Carotid Endarterectomy
If your arteries are blocked, a surgical procedure called a carotid endarterectomy may be necessary to remove the artery’s inner lining.
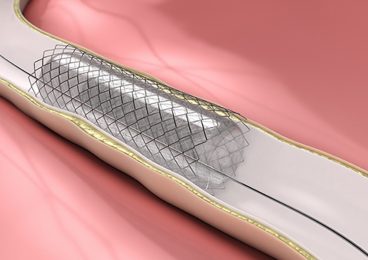
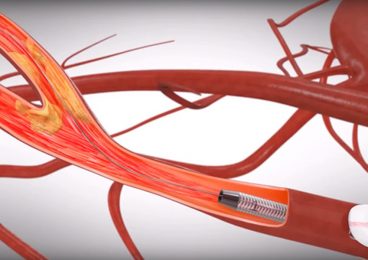
Carotid Artery Angioplasty
Carotid artery angioplasty is a procedure which prevents the artery from narrowing or becoming blocked again by widening the arteries and inserting a stent (tube). In addition, patient tailored or individualized treatment gives the best results, however in some cases, no treatment is necessary. To date, there is no medical treatment of carotid artery disease.